Java Collections Overview
[สรุปภาษาไทย]
การใช้งาน Array ตามปกติของภาษา JAVA
String[] arr = new String[5]; // กำหนด size
String[] arr = new String[]{} // ไม่กำหนด Size
String[] arr = new String[]{"a","b","c","d","e"}; // กำหนด Value ไว้ก่อน
String[][] arr = new String[4][3]; // array 2 มิติกำหนด size
int[][] arr = new int[][]{{55, 66},{77, 88, 99}}; // array 2 มิติกำหนด Value
นอกเหนือจาก StringArray , intArray ?
 |
| img src : http://server2client.com/java6collections/collectionovw.html |
เมื่อเรามองภาพรวมก่อนก็จะเข้าใจได้ว่ามีการแบ่งเป็นหมวดหมู่ดังนี้
Collections - เก็บข้อมูลแบบ Element (ไม่มี key,value)
Map - Map เก็บข้อมูลแบบ Key, Value
Utilities - นำมาใช้จัดการข้อมูลให้ Collections , Map
เริ่มต้นมาดูที่ Collections กันก่อน
 |
| img src : http://server2client.com/java6collections/collectionovw.html |
java.util.Collections
Utilility class ที่ใช้ร่วมกับเหล่า collections
Collection<E>
คือ Root interface ของ Collection
Queue , Set , List เหล่านี้ทำการสืบทอดอีกที (สืบทอดคุณสมบัติ)
ซึ่ง Interfaces เหล่านี้จะมีข้อดี - ข้อเสีย และความเหมาะสมที่จะนำไปใช้งานแตกต่างกันไป
<E> จะหมายถึง Element
หมายถึง Collection ที่เข้าถึงข้อมูลได้จาก Index (ไม่มี key,value)
| Interface/Class | Description |
|---|---|
Collection<E> | Root interface ใน Collection hierarchy ที่ Interfaces : List<E> , Queue<E> , Set<E> ทำการสืบทอด |
List<E> | ordered by the index null-allowed |
Queue<E> | ordered null-allowed |
Set<E> | unique |
ArrayList<E> | ordered By the index random access resizable-array null-allowed |
Vector<E> | multi thread Work (Bitmap..etc) synchronized access random access ordered By the index resizable-array |
LinkedList<E> | ordered By the index fast access doing lots of insert,delete allow null implements Queue interface using pointer providing first-in-first-out queue operations. |
PriorityQueue<E> | ordered and sorted based on priority heap type of queue is PIPO (priority-in, priority-out) elements sorted FIRST are processed first. sorted using a custom comparator. |
HashSet<E> | fast access unordered and unsorted unique use hashmap instance |
LinkedHashSet<E> | ordered fast access ordered set null-allowed |
SortedSet<E> | unique sorted elements. |
TreeSet<E> | implementation of the Set<E> interface using a Treemap instance. sorted [น้อย -> มาก , ตามลำดับอักษร , อื่นๆ ] |
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน ArrayList
ซึ่งเป็น Collection ที่นิยมใช้งานกันอย่างแพร่หลายมาก (คิดอะไรไม่ออกก็ ArrayList)
Iterator method
hasNext( ) , hasPrevious() , next() , nextIndex() , previous() , previousIndex( )
การนำ Collection ตัวอื่นมาเลือกในงานตามความเหมาะสม
เช่น LinkedList เข้ามาเก็บข้อมูลแทน เมื่อข้อมูลชุดนั้นต้องมีการ แก้ไขอยู่บ่อยๆ
LinkedList
LinkedList มี Pointer ที่สามารถคอยชี้ Index ตำแหน่งหัวท้าย
เหมาะกับเก็บกลุ่มข้อมูลที่แก้ไขบ่อยๆ จะทำได้เร็วกว่า Arraylist
method : addLast(); addFirst(); remove(); removeFirst(); removeLast();
หลังจากนี้คุณก็จะเริ่มคิดขึ้นได้ว่า ArrayList ตัวเดียว ไม่เหมาะสม
กับการใช้งานของ Geek อย่างเราแล้วนะ .....
แต่ผมจะขอหยุดไว้เท่านี้เพราะยังไม่มีเวลาศึกษาอย่างลึกซึ้งเช่นกัน (เลือกศึกษาเมื่อต้องใช้งาน)
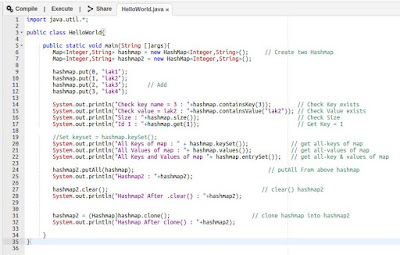
MAP
จะเห็นว่ามีเพียง Map เท่านั้นที่เก็บข้อมูลแบบ <K, V> (key , value)
และอย่าลืมว่า Map ไม่ใช่ Collections และเวลาเพิ่มข้อมูลใส่ใน map จะใช้เมธอท put
แตกต่างจากเหล่า Collections ด้านบนที่ใช้เมธอท add
 |
| img src : http://server2client.com/java6collections/collectionovw.html |
Map Interfaces & Classes
| Interface/Class | Description |
|---|---|
Map<K,V> | Uniqueness |
HashMap<K,V> | fast access set null-allowed |
LinkedHashMap<K,V> | fast access predictable ordering null-allowed |
Hashtable<K,V> | synchronized access |
SortedMap<K,V> | sorted elements. |
TreeMap<K,V> | sorted ordered by natural random access tree unique |
Java Collections Cheatsheet
สำหรับคนที่ศึกษาเรื่อง Collections มาจนปวดหัว
แนะนำให้มองภาพรวมด้วย Cheatsheet ดังนี้
และนำไปเลือกใช้ เลือกศึกษากันตามความเหมาะสมต่อไปครับ ^^
 |
| img src : http://pedrocardoso.eu/scjp-java-collections-cheat-sheet/ |